I have been working in the telecom sector since the early days of fixed access networks, MPLS-based packet cores, GSM, 3G, 4G/LTE, and now the latest wave—5G & AI enhancement. A common question I hear from peers is: “What’s really new in 5G for voice calls, SMS, or even mobile apps?”
The reality is that 5G’s true potential goes far beyond consumer voice and data services. While end-users will experience incremental improvements, 5G is predominantly designed to unlock industrial-scale innovation—enabling use cases such as smart factories, autonomous systems, and large-scale IoT ecosystems.
AI and the Future of Telecom Networks
Artificial intelligence (AI) is emerging as a critical enabler in next-generation RAN deployments and new business models, including neutral host operators, massive IoT connectivity, and mission-critical IoT applications.
The telecom landscape is undergoing a seismic shift, driven by the convergence of 5G and AI. Networks are becoming increasingly complex, and intelligent automation is no longer optional—it is essential. Imagine a network that adapts in real time to user demand, optimizes resource usage instantly, and guarantees seamless connectivity. This is not a futuristic vision; it is already becoming reality.
Dynamic Networks with AI and Machine Learning
With AI at the helm, telecom operators are integrating advanced algorithms into both core and access networks. By continuously analyzing usage patterns, these systems dynamically tune network parameters to match demand.
- Traffic Adaptation: When traffic surges, AI-driven orchestration automatically increases capacity, ensuring performance is maintained without manual intervention.
- Resource Optimization: Idle bandwidth or underutilized resources are dynamically reallocated, improving efficiency across the network.
- Predictive Assurance: AI models forecast potential service degradations before they escalate, enabling proactive intervention and guaranteeing service continuity.
The result is a network that is self-optimizing, resilient, and customer-centric, ultimately boosting user trust and satisfaction.
AI Use Case: Synthetic Alarms and Automated Optimization
In this blog series, I will walk through a practical use case where synthetic alarms are generated to simulate network anomalies. We will then build an AI/ML model that learns from these patterns and triggers corrective actions automatically—optimizing the network without human intervention.
Deploying Kubeflow for Telecom AI
To implement this, I am deploying Kubeflow, a powerful machine learning platform, on top of a Kubernetes cluster. Kubeflow provides the framework for building, training, and deploying ML models that can interact with live network telemetry and automate optimization loops.
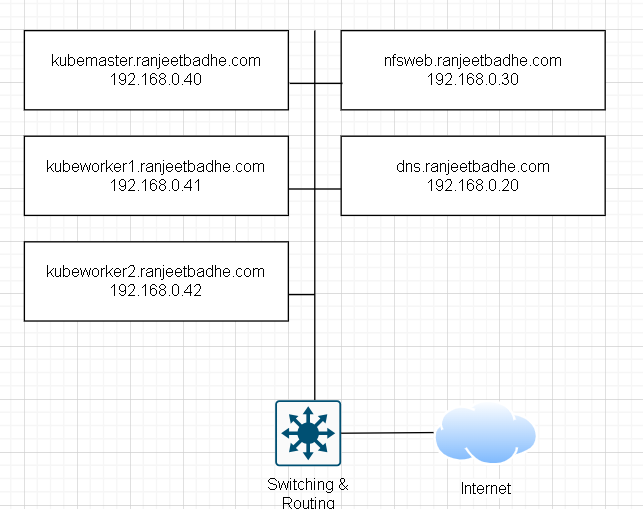
For an on-premises Kubeflow deployment, the following infrastructure components are essential:
- Kubernetes cluster (pre-installed)
- NFS storage for persistence
- Load balancers and routers for service access
- DNS servers for service discovery
I have Kubernetes cluster with single master and 2 worker nodes running on HP DL 380 servers
[root@nfsweb manifests]# kubectl get nodesNAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSIONkubemaster.ranjeetbadhe.com Ready control-plane 10d v1.33.4kubeworker1.ranjeetbadhe.com Ready mazdoor,worker 10d v1.33.4kubeworker2.ranjeetbadhe.com Ready mazdoor,worker 10d v1.33.4
The first step is to install the Git command-line tool on my system. Once Git is available, I proceed to clone the kubesoft repository, which downloads all the source code and project history to my local environment.Install Git. Kubeflow is a Kubernetes-native MLOps platform that streamlines the entire machine learning lifecycle—training, tuning, deployment, and monitoring—on scalable, cloud-native infrastructure. Built on Kubernetes CRDs and operators, it integrates components like Pipelines for workflow automation, KServe for model serving, and Katib for hyperparameter optimization. Its modular, portable design enables reproducible ML at scale across on-prem, hybrid, and multi-cloud environments, making it a strategic choice for enterprise-grade AI deployments
[root@nfsweb ~]# dnf install git -yUpdating Subscription Management repositories.Last metadata expiration check: 3:16:38 ago on Fri 19 Sep 2025 03:23:01 AM UTC.Dependencies resolved.================================================================================================== Package Architecture Version ==================================================================================================Installing: git x86_64 2.47.3-1.el9_6 Installing dependencies: git-core x86_64 2.47.3-1.el9_6 git-core-doc noarch 2.47.3-1.el9_6 perl-Error noarch 1:0.17029-7.el9 perl-Git noarch 2.47.3-1.el9_6 perl-TermReadKey x86_64 2.38-11.el9 perl-lib x86_64 0.65-481.1.el9_6
Transaction Summary==================================================================================================Install 7 Packages
[root@nfsweb ~]# git clone https://github.com/kubeflow/manifests.gitCloning into 'manifests'...remote: Enumerating objects: 34742, done.remote: Counting objects: 100% (648/648), done.remote: Compressing objects: 100% (456/456), done.remote: Total 34742 (delta 422), reused 192 (delta 192), pack-reused 34094 (from 3)Receiving objects: 100% (34742/34742), 47.33 MiB | 6.98 MiB/s, done.Resolving deltas: 100% (20657/20657), done.
[root@nfsweb ~]# cd manifests/[root@nfsweb manifests]# while ! kustomize build example | kubectl apply --server-side --force-conflicts -f -; do echo "Retrying to apply resources"; sleep 20; done# Warning: 'vars' is deprecated. Please use 'replacements' instead. [EXPERIMENTAL] Run 'kustomize edit fix' to update your Kustomization automatically.# Warning: 'patchesStrategicMerge' is deprecated. Please use 'patches' instead. Run 'kustomize edit fix' to update your Kustomization automatically.
validatingwebhookconfiguration.admissionregistration.k8s.io/pvcviewer-validating-webhook-configuration serverside-appliedvalidatingwebhookconfiguration.admissionregistration.k8s.io/servingruntime.serving.kserve.io serverside-appliedvalidatingwebhookconfiguration.admissionregistration.k8s.io/spark-operator-webhook serverside-appliedvalidatingwebhookconfiguration.admissionregistration.k8s.io/trainedmodel.serving.kserve.io serverside-appliedvalidatingwebhookconfiguration.admissionregistration.k8s.io/validation.webhook.serving.knative.dev serverside-appliedvalidatingwebhookconfiguration.admissionregistration.k8s.io/validator.trainer.kubeflow.org serverside-applied[root@nfsweb manifests]#
[root@nfsweb manifests]# kubectl get nsNAME STATUS AGEargocd Active 4h21mauth Active 34mcalico-apiserver Active 10dcalico-system Active 10dcert-manager Active 34mdefault Active 10distio-system Active 34mknative-serving Active 34mkube-node-lease Active 10dkube-public Active 10dkube-system Active 10dkubeflow Active 34mkubeflow-system Active 34mkubeflow-user-example-com Active 18mnfs-provisioner Active 9doauth2-proxy Active 34mtigera-operator Active 10d
[root@nfsweb manifests]# kubectl get ns --sort-by=.metadata.creationTimestamp \| awk 'NR==1{print; next} {a[NR]=$0} END{for(i=NR;i>1;i--) print a[i]}'NAME STATUS AGEkubeflow-user-example-com Active 22mauth Active 38moauth2-proxy Active 38mistio-system Active 38mkubeflow-system Active 38mkubeflow Active 38mknative-serving Active 38mcert-manager Active 38margocd Active 4h25mnfs-provisioner Active 9dcalico-system Active 10dcalico-apiserver Active 10dtigera-operator Active 10dkube-node-lease Active 10ddefault Active 10dkube-public Active 10dkube-system Active 10d
Here is a privildge pod security shell script which will find out on which namespaces have ISTIO injection enabled on them
on those namespaces it adds 2 node labels which allows them to have extra permissions.
[root@nfsweb manifests]# vi security.sh[root@nfsweb manifests]# chmod +x security.sh[root@nfsweb manifests]# cat security.sh#!/usr/bin/env bashset -euo pipefail
# Find all namespaces with Istio injection enablednamespaces=$(kubectl get ns \ -l istio-injection=enabled \ -o jsonpath='{.items[*].metadata.name}')
if [[ -z "$namespaces" ]]; then echo "No namespaces found with istio-injection=enabled" exit 1fi
for ns in $namespaces; do echo "→ Updating PodSecurity on namespace \"$ns\"" kubectl label namespace "$ns" \ pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce=privileged \ pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce-version=latest \ --overwrite
echo "→ Restarting all deployments in \"$ns\"" kubectl rollout restart deployment -n "$ns"done
echo "✅ Done."
Kubernetes base AI
[root@nfsweb manifests]# sh security.sh→ Updating PodSecurity on namespace "knative-serving"namespace/knative-serving labeled→ Restarting all deployments in "knative-serving"deployment.apps/activator restarteddeployment.apps/autoscaler restarteddeployment.apps/controller restarteddeployment.apps/net-istio-controller restarteddeployment.apps/net-istio-webhook restarteddeployment.apps/webhook restarted→ Updating PodSecurity on namespace "kubeflow"namespace/kubeflow labeled→ Restarting all deployments in "kubeflow"deployment.apps/admission-webhook-deployment restarteddeployment.apps/cache-server restarteddeployment.apps/centraldashboard restarteddeployment.apps/jupyter-web-app-deployment restarteddeployment.apps/katib-controller restarteddeployment.apps/katib-db-manager restarteddeployment.apps/katib-mysql restarteddeployment.apps/katib-ui restarteddeployment.apps/kserve-controller-manager restarteddeployment.apps/kserve-localmodel-controller-manager restarteddeployment.apps/kserve-models-web-app restarteddeployment.apps/kubeflow-pipelines-profile-controller restarteddeployment.apps/metadata-envoy-deployment restarteddeployment.apps/metadata-grpc-deployment restarteddeployment.apps/metadata-writer restarteddeployment.apps/minio restarteddeployment.apps/ml-pipeline restarteddeployment.apps/ml-pipeline-persistenceagent restarteddeployment.apps/ml-pipeline-scheduledworkflow restarteddeployment.apps/ml-pipeline-ui restarteddeployment.apps/ml-pipeline-viewer-crd restarteddeployment.apps/ml-pipeline-visualizationserver restarteddeployment.apps/mysql restarteddeployment.apps/notebook-controller-deployment restarteddeployment.apps/profiles-deployment restarteddeployment.apps/pvcviewer-controller-manager restarteddeployment.apps/seaweedfs restarteddeployment.apps/spark-operator-controller restarteddeployment.apps/spark-operator-webhook restarteddeployment.apps/tensorboard-controller-deployment restarteddeployment.apps/tensorboards-web-app-deployment restarteddeployment.apps/volumes-web-app-deployment restarteddeployment.apps/workflow-controller restarted→ Updating PodSecurity on namespace "kubeflow-system"namespace/kubeflow-system labeled→ Restarting all deployments in "kubeflow-system"deployment.apps/jobset-controller-manager restarteddeployment.apps/kubeflow-trainer-controller-manager restarted→ Updating PodSecurity on namespace "kubeflow-user-example-com"namespace/kubeflow-user-example-com labeled→ Restarting all deployments in "kubeflow-user-example-com"No resources found in kubeflow-user-example-com namespace.✅ Done.
istio-ingressgateway is created ,next we configure Metallb load balancer for external access.
[root@nfsweb manifests]# kubectl get svc -n istio-systemNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGEcluster-local-gateway ClusterIP 10.111.195.133 15020/TCP,80/TCP 131mistio-ingressgateway ClusterIP 10.96.228.44 15021/TCP,80/TCP,443/TCP 131mistiod ClusterIP 10.104.238.195 15010/TCP,15012/TCP,443/TCP,15014/TCP 131mknative-local-gateway ClusterIP 10.105.185.81 80/TCP,443/TCP 131m
Accessing the applications ,lets configure
[root@nfsweb manifests]# kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/metallb/metallb/v0.14.8/config/manifests/metallb-native.yamlnamespace/metallb-system createdcustomresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bfdprofiles.metallb.io createdcustomresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgpadvertisements.metallb.io createdcustomresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgppeers.metallb.io createdcustomresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/communities.metallb.io createdcustomresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipaddresspools.metallb.io createdcustomresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/l2advertisements.metallb.io createdcustomresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/servicel2statuses.metallb.io createdserviceaccount/controller createdserviceaccount/speaker createdrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/controller createdrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/pod-lister createdclusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metallb-system:controller createdclusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metallb-system:speaker createdrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/controller createdrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/pod-lister createdclusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metallb-system:controller createdclusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metallb-system:speaker createdconfigmap/metallb-excludel2 created[root@nfsweb manifests]# kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/metallb/metallb/v0.14.8/config/manifests/metallb-native.yaml
namespace/metallb-system created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bfdprofiles.metallb.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgpadvertisements.metallb.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgppeers.metallb.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/communities.metallb.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipaddresspools.metallb.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/l2advertisements.metallb.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/servicel2statuses.metallb.io created
serviceaccount/controller created
serviceaccount/speaker created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/controller created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/pod-lister created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metallb-system:controller created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metallb-system:speaker created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/controller created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/pod-lister created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metallb-system:controller created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metallb-system:speaker created
configmap/metallb-excludel2 created
secret/metallb-webhook-cert created
service/metallb-webhook-service created
deployment.apps/controller created
daemonset.apps/speaker created
validatingwebhookconfiguration.admissionregistration.k8s.io/metallb-webhook-configuration created
[root@nfsweb manifests]# kubectl apply -f metal-lb-manifest.yaml
ipaddresspool.metallb.io/default-pool created
l2advertisement.metallb.io/default-l2 createdsecret/metallb-webhook-cert createdservice/metallb-webhook-service createddeployment.apps/controller createddaemonset.apps/speaker createdvalidatingwebhookconfiguration.admissionregistration.k8s.io/metallb-webhook-configuration created
[root@nfsweb manifests]# cat metal-lb-manifest.yamlapiVersion: metallb.io/v1beta1kind: IPAddressPoolmetadata: name: default-pool namespace: metallb-systemspec: addresses: - 192.168.0.220-192.168.0.240---apiVersion: metallb.io/v1beta1kind: L2Advertisementmetadata: name: default-l2 namespace: metallb-systemspec: ipAddressPools: - default-pool
#apiVersion: v1kind: Servicemetadata: creationTimestamp: "2025-09-19T06:57:05Z" labels: app: istio-ingressgateway app.kubernetes.io/instance: istio app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm app.kubernetes.io/name: istio-ingressgateway app.kubernetes.io/part-of: istio app.kubernetes.io/version: 1.27.0 helm.sh/chart: istio-ingress-1.27.0 install.operator.istio.io/owning-resource: unknown istio: ingressgateway istio.io/rev: default operator.istio.io/component: IngressGateways release: istio name: istio-ingressgateway namespace: istio-system resourceVersion: "293386" uid: be5a6a8c-ac11-4090-bd5a-4b26bc02d71dspec: clusterIP: 10.96.228.44 clusterIPs: - 10.96.228.44 internalTrafficPolicy: Cluster ipFamilies: - IPv4 ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack ports: - name: status-port port: 15021 protocol: TCP targetPort: 15021 - name: http2 port: 80 protocol: TCP targetPort: 8080 - name: https port: 443 protocol: TCP targetPort: 8443 selector: app: istio-ingressgateway istio: ingressgateway sessionAffinity: None type: ClusterIP (Changed to LoadBalancer)status: loadBalancer: {}
Configuration changed to LoadBalancer from Cluster
apiVersion: v1kind: Servicemetadata: annotations: metallb.universe.tf/ip-allocated-from-pool: default-pool creationTimestamp: "2025-09-19T06:57:05Z" labels: app: istio-ingressgateway app.kubernetes.io/instance: istio app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm app.kubernetes.io/name: istio-ingressgateway app.kubernetes.io/part-of: istio app.kubernetes.io/version: 1.27.0 helm.sh/chart: istio-ingress-1.27.0 install.operator.istio.io/owning-resource: unknown istio: ingressgateway istio.io/rev: default operator.istio.io/component: IngressGateways release: istio name: istio-ingressgateway namespace: istio-system resourceVersion: "385322" uid: be5a6a8c-ac11-4090-bd5a-4b26bc02d71dspec: allocateLoadBalancerNodePorts: true clusterIP: 10.96.228.44 clusterIPs: - 10.96.228.44 externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster internalTrafficPolicy: Cluster ipFamilies: - IPv4 ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack ports: - name: status-port nodePort: 30556 port: 15021 protocol: TCP targetPort: 15021 - name: http2 nodePort: 32547 port: 80 protocol: TCP targetPort: 8080 - name: https nodePort: 30103 port: 443 protocol: TCP targetPort: 8443 selector: app: istio-ingressgateway istio: ingressgateway sessionAffinity: None type: LoadBalancerstatus: loadBalancer: ingress: - ip: 192.168.0.220 ipMode: VIP
Changing the Kubeflow settings
#apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1kind: Gatewaymetadata: creationTimestamp: "2025-09-19T06:58:09Z" generation: 1 name: kubeflow-gateway namespace: kubeflow resourceVersion: "295072" uid: 099a06a8-d72c-467b-9769-cee2f03259b1spec: selector: istio: ingressgateway servers: - hosts: - '*' port: name: http number: 80 protocol: HTTP
# HTTPS listener port: number: 443 name: https protocol: HTTPS tls: mode: SIMPLE credentialName: kubeflow-ingressgateway-certs hosts: - "*"
Loadbalancer
[root@nfsweb manifests]# kubectl get svc -n istio-systemNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGEcluster-local-gateway ClusterIP 10.111.195.133 15020/TCP,80/TCP 3h31mistio-ingressgateway LoadBalancer 10.96.228.44 192.168.0.220 15021:30556/TCP,80:32547/TCP,443:30103/TCP 3h31mistiod ClusterIP 10.104.238.195 15010/TCP,15012/TCP,443/TCP,15014/TCP 3h31mknative-local-gateway ClusterIP 10.105.185.81 80/TCP,443/TCP 3h31m
We got the external ip 192.168.0.220 for access.
Accessing the GUI
. With the deployment complete, our next episode will dive into the exciting part—building, training, and deploying machine learning models that can actively interact with live network telemetry. These models will process SNMP alarms and data flowing in through southbound protocols to enable automated, closed-loop optimization. To illustrate the concept clearly, we’ll start with a synthetic alarm as our use case before scaling toward real-world scenarios
Kubeflow Cluster Deployments – With Namespaces and Purpose
| Namespace | Deployment | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| auth | dex | OIDC identity provider used for authentication (e.g., GitHub, LDAP, Google). |
| oauth2-proxy | oauth2-proxy | Acts as a reverse proxy, handling OAuth2-based login and token exchange for web UIs. |
| cert-manager | cert-manager | Manages TLS certificates (e.g., from Let’s Encrypt) for secure ingress. |
| cert-manager | cert-manager-cainjector | Injects CA data into webhook configurations automatically. |
| cert-manager | cert-manager-webhook | Handles dynamic admission control for cert-manager resources. |
| default | nfs-provisioner-nfs-subdir-external-provisioner | Dynamic NFS-based storage provisioning using sub-directories. |
| istio-system | cluster-local-gateway | Istio gateway for internal-only traffic between services. |
| istio-system | istio-ingressgateway | External-facing Istio gateway handling ingress traffic. |
| istio-system | istiod | Istio control plane: manages sidecars, traffic rules, certificates. |
| knative-serving | activator | Buffers requests for scale-to-zero services until pods are ready. |
| knative-serving | autoscaler | Monitors traffic and scales Knative services up/down. |
| knative-serving | controller | Reconciles Knative Serving CRDs like Revision, Service. |
| knative-serving | net-istio-controller | Integrates Knative networking with Istio for traffic routing. |
| knative-serving | net-istio-webhook | Admission webhook for validating Istio networking resources. |
| knative-serving | webhook | Validates and mutates Knative resources at creation. |
| kube-system | coredns | Internal DNS server for Kubernetes service discovery. |
| kubeflow-user-example-com | ml-pipeline-ui-artifact | UI to view pipeline artifacts. |
| kubeflow-user-example-com | ml-pipeline-visualizationserver | Renders charts/visuals of metrics during pipeline run. |
| kubeflow | admission-webhook-deployment | Validates resources like notebooks before they’re created. |
| kubeflow | cache-server | Caches pipeline steps to avoid redundant executions. |
| kubeflow | centraldashboard | The main UI for accessing Kubeflow features. |
| kubeflow | jupyter-web-app-deployment | UI for managing and spawning Jupyter notebooks. |
| kubeflow | katib-controller | Manages experiment lifecycle. |
| kubeflow | katib-db-manager | Seeds Katib DB schema and manages connections. |
| kubeflow | katib-mysql | MySQL database to store experiments and trials. |
| kubeflow | katib-ui | Web UI to launch and view Katib experiments. |
| kubeflow | kserve-controller-manager | Main controller for managing InferenceService CRDs. |
| kubeflow | kserve-localmodel-controller-manager | For serving models from local storage. |
| kubeflow | kserve-models-web-app | Web UI to manage deployed models. |
| kubeflow | kubeflow-pipelines-profile-controller | Ties pipelines with user profiles and RBAC. |
| kubeflow | metadata-envoy-deployment | Sidecar proxy for metadata API. |
| kubeflow | metadata-grpc-deployment | gRPC API server for metadata tracking. |
| kubeflow | metadata-writer | Writes pipeline metadata for lineage tracking. |
| kubeflow | minio | S3-compatible object store used to store pipeline artifacts, models, etc. |
| kubeflow | ml-pipeline | Orchestrates pipeline execution and lifecycle. |
| kubeflow | ml-pipeline-persistenceagent | Persists pipeline runs and metadata to DB. |
| kubeflow | ml-pipeline-scheduledworkflow | Handles scheduled/cron-based pipeline runs. |
| kubeflow | ml-pipeline-ui | Web UI to browse and run ML pipelines. |
| kubeflow | ml-pipeline-viewer-crd | Manages CRD for artifact viewer and rendering logic. |
| kubeflow | ml-pipeline-visualizationserver | Renders charts/visuals of metrics during pipeline run. |
| kubeflow | mysql | Relational DB backend used by Katib for experiment metadata. |
| kubeflow | notebook-controller-deployment | Controller for managing notebook CRDs (spawns pods). |
| kubeflow | profiles-deployment | Manages user profiles, namespaces, and isolation. |
| kubeflow | pvcviewer-controller-manager | Renders UI to view contents of PVCs in the dashboard. |
| kubeflow | spark-operator-controller | Manages Spark applications and jobs on K8s. |
| kubeflow | spark-operator-webhook | Validates Spark job submissions. |
| kubeflow | tensorboard-controller-deployment | Manages tensorboard instances tied to experiments. |
| kubeflow | tensorboards-web-app-deployment | UI for launching and browsing tensorboards. |
| kubeflow | training-operator | Custom controller for training jobs (TFJob, PyTorchJob, etc.). |
| kubeflow | volumes-web-app-deployment | Web UI to manage PVCs in the user’s namespace. |
| kubeflow | workflow-controller | Argo controller that runs workflows in Kubernetes. |
| metallb-system | controller | Manages allocation of external IPs for services using MetalLB. |